How Diet and Exercise Impact Osteoarthritis
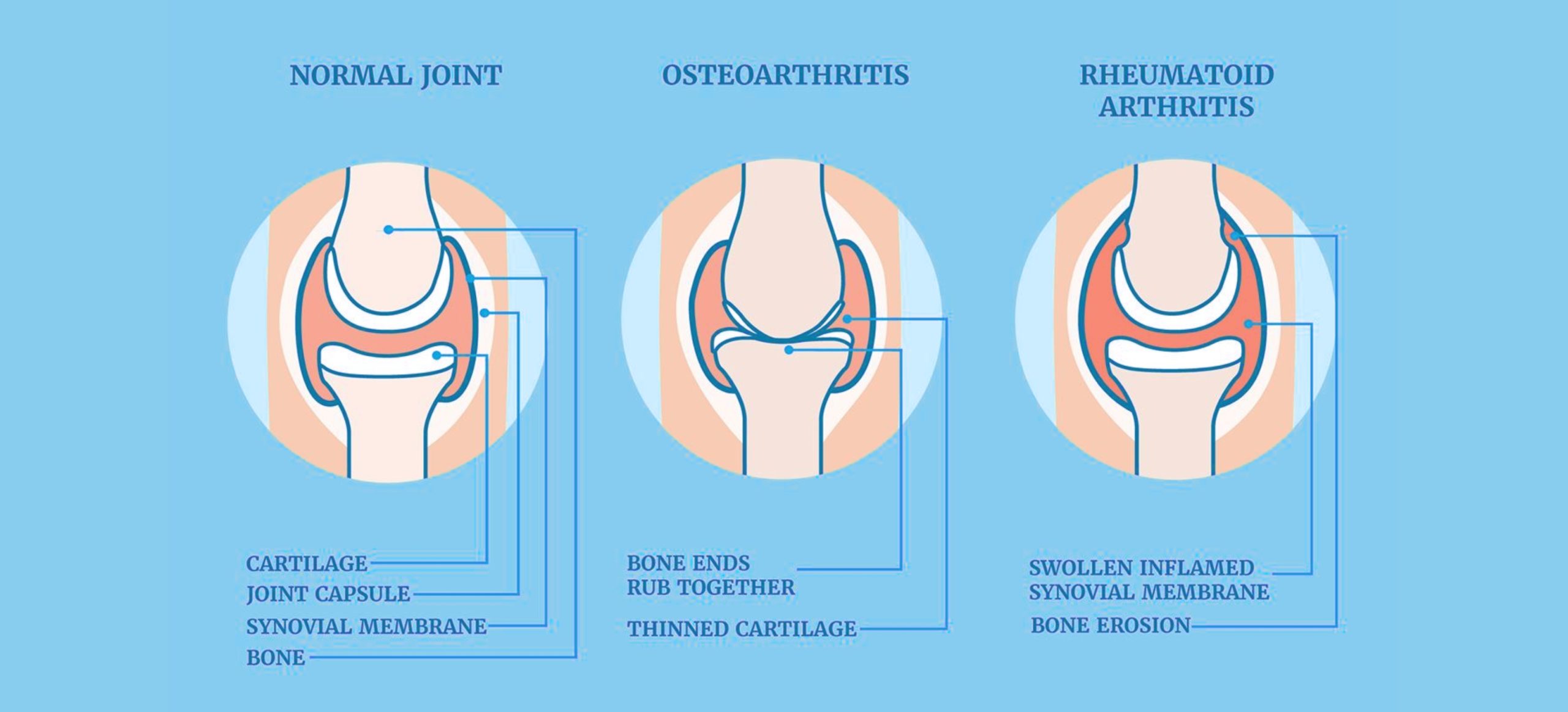
Osteoarthritis (OA), a degenerative joint disease, affects millions worldwide and can significantly impact quality of life. While there is no definitive cure, lifestyle modifications, including diet and exercise, have proven effective in managing symptoms and slowing disease progression.
Understanding Osteoarthritis and Lifestyle Choices
Osteoarthritis is characterized by the breakdown of cartilage in the joints, leading to pain, stiffness, and decreased mobility. Factors such as aging, obesity, joint injuries, and genetic predisposition can contribute to its development. While medical treatments such as pain relievers and physical therapy are often prescribed, integrating healthy lifestyle choices, like a balanced diet and regular exercise, plays a crucial role in alleviating symptoms and enhancing overall well-being.
The Role of Diet in Managing Osteoarthritis
A well-planned diet can help reduce inflammation, promote joint health, and manage weight, key factors in controlling osteoarthritis symptoms.
Anti-Inflammatory Foods
Inflammation exacerbates osteoarthritis symptoms, making anti-inflammatory foods an essential component of an OA-friendly diet. Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon, mackerel, and walnuts, help combat inflammation. Additionally, incorporating turmeric, known for its active compound curcumin, may provide significant relief from joint pain and stiffness.
Foods Rich in Antioxidants
Oxidative stress can accelerate joint damage in osteoarthritis patients. Antioxidant-rich foods, such as berries, leafy greens, and citrus fruits, help neutralize free radicals and protect joint tissues. Vitamin C, found in oranges and strawberries, is particularly beneficial for cartilage repair and maintenance.
Maintaining a Healthy Weight
Excess weight puts additional stress on weight-bearing joints like the knees and hips, worsening osteoarthritis symptoms. A diet focused on portion control, whole grains, lean proteins, and vegetables aids in weight management, reducing joint strain and slowing disease progression.
The Benefits of Exercise for Osteoarthritis Patients
Exercise is often misunderstood as a potential aggravator of osteoarthritis. However, the right type and intensity of physical activity can bring numerous benefits.
Improving Joint Mobility and Flexibility
Gentle exercises such as yoga and tai chi enhance flexibility and maintain joint mobility, helping patients perform daily activities with ease. Stretching exercises also reduce stiffness, a common challenge for those with OA.
Strengthening Muscles Around Joints
Strengthening the muscles surrounding affected joints provides better support and stability, reducing pain and minimizing the risk of injury. Targeted exercises for the quadriceps, hamstrings, and hip muscles are particularly beneficial for knee osteoarthritis.
Reducing Pain and Stiffness
Regular movement boosts the production of synovial fluid, which lubricates joints and reduces pain. Low-impact activities like swimming and cycling are especially effective in relieving stiffness without causing additional joint strain.
Recommended Diets for Osteoarthritis
Certain dietary patterns are particularly effective in managing osteoarthritis symptoms due to their anti-inflammatory and weight-control benefits.
Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean diet emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, olive oil, and lean proteins. Its focus on anti-inflammatory and antioxidant-rich foods makes it an ideal choice for osteoarthritis management.
DASH Diet
The DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet, known for reducing hypertension, also supports joint health. By promoting fresh produce, low-fat dairy, lean proteins, and whole grains, it limits inflammatory agents such as added sugars and trans fats. This balanced diet aids in maintaining a healthy weight, further alleviating joint strain.
Plant-Based Diet
A predominantly plant-based diet that includes legumes, nuts, seeds, and whole grains can help reduce inflammation while providing vital nutrients like magnesium and potassium, which are essential for bone and joint health. Reducing or eliminating red meat, which can contribute to inflammation, further supports joint function.
Gluten-Free Diet
Some osteoarthritis patients report symptom relief by eliminating gluten, particularly if they have a sensitivity or intolerance. A gluten-free diet, rich in naturally gluten-free foods like quinoa, rice, fruits, and vegetables, minimizes inflammation while enhancing nutrient intake.
Low-Carb or Ketogenic Diet
Low-carb and ketogenic diets focus on reducing carbohydrate intake and increasing healthy fats and proteins. This approach helps with weight loss and decreases systemic inflammation, making it a potential choice for osteoarthritis management. Healthy fats from avocados, nuts, and olive oil are particularly beneficial.
Safe Exercises for Osteoarthritis
Choosing appropriate exercises tailored to individual capabilities and joint conditions is essential for managing osteoarthritis effectively.
Low-Impact Aerobics
Low-impact aerobic activities like walking, cycling, and water aerobics improve cardiovascular health and aid in weight management without placing undue stress on joints. Swimming, in particular, is highly recommended for its joint-friendly nature.
Strength Training
Strength training exercises using resistance bands or light weights build muscle strength and enhance joint stability. Working with a physical therapist or fitness expert ensures that these exercises are performed safely.
Flexibility and Stretching Exercises
Stretching exercises, such as hamstring stretches and gentle yoga poses, enhance flexibility, reduce stiffness, and improve overall mobility. Daily stretching routines can make a noticeable difference in managing osteoarthritis symptoms.
Combining Diet and Exercise for Effective Osteoarthritis Management
A holistic approach that combines diet and exercise yields the best results in osteoarthritis management. For example, a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods complements the pain-relieving and mobility-enhancing effects of exercise. Together, these lifestyle changes create a synergistic effect, reducing joint stress, inflammation, and the progression of osteoarthritis.
Tips for Starting and Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle with Osteoarthritis
Adopting a healthy lifestyle with osteoarthritis requires patience and a structured approach. Start by setting realistic goals, focusing on manageable changes like incorporating one new exercise or dietary habit at a time, as gradual adjustments are more sustainable. Seeking professional guidance from dietitians or physical therapists ensures your routine is tailored to your specific needs. Consistency is crucial; regular exercise and a balanced diet must become part of your daily life for long-term benefits. Additionally, tracking progress through a journal can help monitor improvements in pain, flexibility, and overall well-being, keeping you motivated and on course.
FAQ
Yes, certain foods can worsen inflammation, including processed foods, sugary beverages, and trans fats. Reducing or eliminating these from your diet can alleviate symptoms.
Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the stress on weight-bearing joints like the knees and hips, decreasing pain and slowing the progression of osteoarthritis.
Anti-inflammatory foods, such as fatty fish, turmeric, and green leafy vegetables, help reduce inflammation, easing pain and stiffness in affected joints.
Yes, strength training is safe when done correctly. It strengthens muscles around joints, providing stability and reducing joint strain. Always consult a professional before starting a new routine.
A consistent routine of moderate exercise, about 30 minutes a day, five times a week, is beneficial. Start slow and listen to your body, gradually increasing intensity as tolerated.
Categories
Company
Media
Follow Us
© Copyright Biotech /Terms Of Use - Privacy Policy
Version 2_CT_1212222
